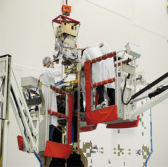
 SES has integrated a NASA instrument payload equipped with an ultraviolet imaging spectrograph onto the company’s SES-14 geostationary communications satellite.
SES has integrated a NASA instrument payload equipped with an ultraviolet imaging spectrograph onto the company’s SES-14 geostationary communications satellite.
The Global-Scale Observations of the Limb and Disk instrument’s spectrograph is designed to measure temperatures and densities in the Earth’s ionosphere and thermosphere to investigate ionospheric disruptions to navigation and communication transmissions, SES said Tuesday.
SES-14 is built to provide C– and Ku-band wide beam and high-throughput satellite services over Western Europe, Americas, Northwest Africa and Atlantic Ocean.
Airbus’ defense and space business developed the SES-14 satellite, while the University of Colorado’s laboratory for atmospheric and space physics built the GOLD instrument.
SES Government Solutions subsidiary and its parent company will provide science data and missions operations support in addition to the host satellite.
The Florida Space Institute at the University of Central Florida serves as principal investigator and NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Maryland provides overall program management support for the project.
The satellite and the GOLD instrument are in the testing phase in France.
NASA and SES plan to launch the satellite with the hosted payload aboard a SpaceX-built Falcon 9 rocket from Cape Canaveral in Florida later this year.




