At its core, the Air Force Zero Trust is the military’s response to high-profile cyber attacks. Recognizing the need to bolster cybersecurity defenses, the U.S. Air Force has initiated efforts to implement the zero-trust security framework.
Let’s take a closer look at this security model, focusing on its principles, benefits, and effects on the U.S. Air Force.
What is Zero Trust and How Does it Work

Conceptualized by John Kindervag in 2010, zero trust is a security framework safeguarding infrastructures and sensitive data from internal and external threats. It guarantees that the interactions within the network comply with security policies.
The model mitigates cybersecurity risks using three core principles rooted in the “never trust; always verify” philosophy: (1) assume breach; (2) verify continuously; and (3) grant least privilege access.
Zero trust treats all entities and activities as suspicious, always ready to attack and counterattack potential threats. It doesn’t rely on initial authentication but rather constantly assesses and verifies the network’s users, devices, and activities.
Furthermore, it enforces strict access controls to minimize potential damage in case of a security breach. It narrows down access permissions to the resources needed to carry out specific tasks.
Why Adopt a Zero Trust Framework
In the past, organizations relied on traditional perimeter security strategies, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and VPNs. While these components offer some level of security, they are no longer adequate to combat advanced cybersecurity threats, ransomware attacks, phishing, and data breaches.
Zero Trust uses an identity-centric approach to cater to the security requirements of the data-centric hybrid cloud setting. This extends security measures to remote endpoints and the Internet of Things (IoT) devices, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches.
Unlike the Zero Trust model, which inspects all entities within a network, the old perimeter security model considers all entities inside the network trustworthy, leading to network vulnerabilities. That said, the new security framework is more suited for today’s advanced security needs, given the rise of cloud computing, IoT, and remote workforces.
How Zero Trust Affects US Air Force’s Cyber Defense
As the importance of Zero Trust in military cybersecurity increases, the US Air Force proactively restructures its cyber defense strategies. Below, we’ll discuss the effect of the new security model on the Air Force’s cyber defense, its rollout process, and strategic roadmaps.
Executive Order Directives on Cyber Defense
The White House issued the Executive Order in May 2021 urging federal agencies to transition to a zero-trust strategy. It marks a shift in priorities for US cybersecurity.
The Biden administration’s strategy prioritizes the prevention, detection, assessment, and remediation of cyber incidents for national defense and economic security. As part of the implementation, government organizations must follow the guidelines stipulated in NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) Special Publication 800-207.
Following the Executive Order, NIST 800-207 underwent rigorous validation processes. As a result, it has been regarded as the default standard for zero-trust implementation, even among private enterprises.
Implementation of Zero Trust in US Air Force Cybersecurity
For the Department of the Air Force, zero trust application means more than simple compliance with the administration’s directives. The agency has been actively integrating this framework into its cyber defense architecture for several years.
An example of the U.S. Air Force’s adoption of the new model is the security of flight line operations. Traditionally, data exchange within the flight line involved manual transfer via portable drives among aircraft, maintenance areas, and central repositories.
Pillars and Roadmaps for US Air Force Zero Trust Adoption
Spearheaded by Justin Stolpman, Director of the Air Force’s Zero Trust Functional Management Office, the agency released its Zero Trust Implementation Roadmap in 2023. This roadmap aligns with the directives of the Executive Order and Zero Trust principles.
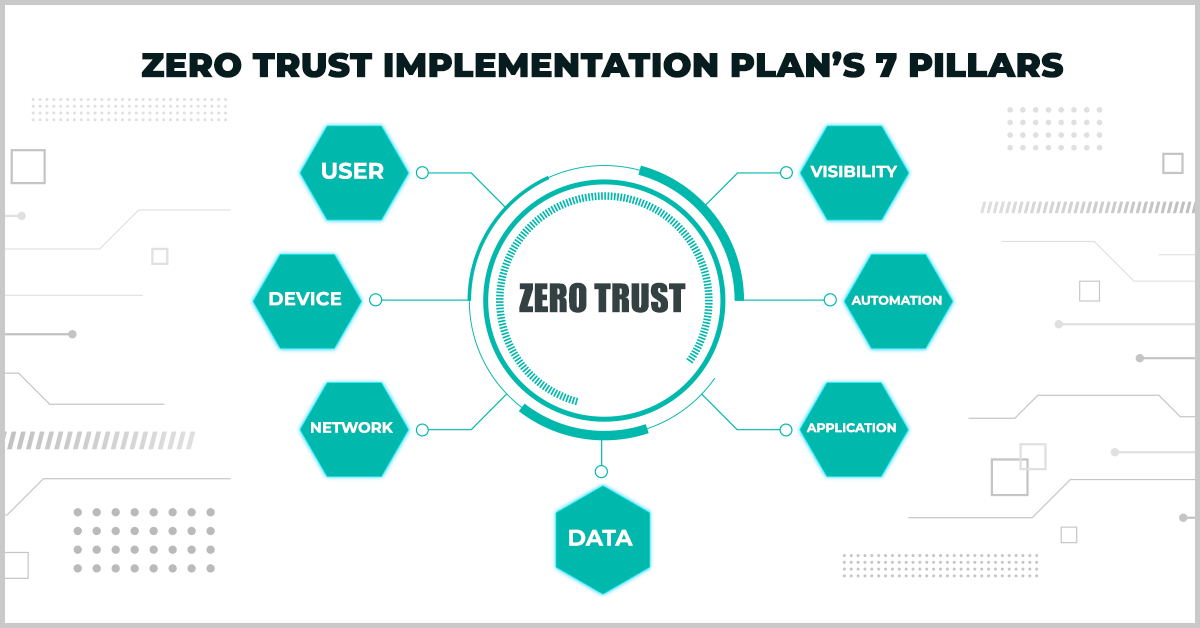
The US Air Force’s roadmap follows the various components of the DoD strategy for reporting purposes, focusing on seven pillars to stay unified at the DOD strategic level. It includes seven pillars:
- User
- Device
- Network
- Data
- Application
- Automation
- Visibility
Each domain is analyzed from the current state to the end state. It also highlights gaps, challenges, and actionable metrics needed to carry through a zero-trust framework.
Moreover, the framework limits access to sensitive data and systems to prevent adversaries from infiltrating Air Force networks. In return, it allows Air Force cybersecurity teams to monitor and identify suspicious behavior in real-time.
In the long run, the integration of zero trust principles is to pave the way for modernization within the Air Force’s information technology systems and amplify the agency’s cyber defense strategies.
As cyber threats continue to advance, Zero Trust will remain an integral component of the US military’s defense strategy.
Join us at the 2024 Air Force Summit in July 2024 and learn more about the federal agency’s defense efforts. Register now.





